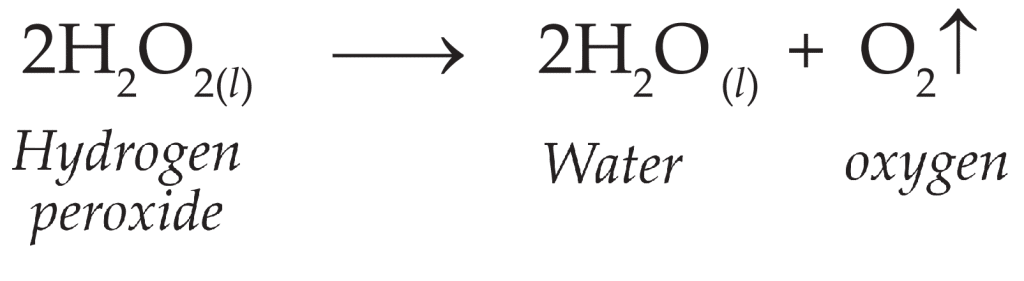How Does pH Affect Catalase Activity?
Download a PDF Copy of This Experiment!
Objective
To determine how pH affects the enzymatic activity of catalase in potato tissue.
Background
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to occur. Catalase is an important enzyme found in nearly all aerobic organisms, including plants, animals, and bacteria. Its primary function is to protect cells from oxidative damage by breaking down hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), a toxic byproduct of metabolic processes, into harmless water (H₂O) and oxygen (O₂), as shown in the reaction below:
Hydrogen peroxide is produced naturally in cells as a result of metabolic reactions such as cellular respiration. If not broken down, it can cause oxidative stress, leading to cell damage and dysfunction. Catalase, which is present in high concentrations in tissues such as the liver and potatoes, rapidly decomposes hydrogen peroxide into non-toxic components.
Enzyme activity is highly dependent on environmental factors such as temperature and pH. The structure of enzymes, including catalase, is made up of proteins, which can be altered by changes in pH. Enzymes have an optimal pH range where they function most efficiently. When the pH deviates too far from this optimal range, the enzyme’s structure, particularly its active site, may be altered, reducing its ability to bind to substrates effectively. This process is known as denaturation.
For catalase in potato tissue, the reported optimum pH is around 7.0, meaning it works most efficiently under neutral conditions. However, in this experiment, we will investigate how varying pH levels affect the enzyme's ability to catalyze the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. By measuring the oxygen released during the reaction using an oxygen detection system, we can assess the enzyme's activity under different pH conditions.
This experiment will help demonstrate the importance of pH in enzymatic reactions and its impact on biological processes. Understanding how pH influences enzyme activity has practical applications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and food science, where enzyme function plays a critical role in biochemical processes.
Materials
Potato
Distilled water
Hydrogen peroxide (3%)
pH meter
Vernier LabQuest Apparatus (O2 Sensor + Labquest Computer Interface + Nalgene Bottle)
Stirring rod
Pipette (1 ml)
Digital scale
Sodium hydroxide (0.1 M)
Hydrochloric acid (0.1 M)
Download a PDF Copy of This Experiment!
Procedure
Preparation of Potato Pulp Samples (Completed by Instructor Before Class)
Peel and chop fresh potatoes into small pieces.
Weigh out an equal ratio of chopped potatoes to distilled water (e.g., 200 g potatoes with 200 mL water) to achieve at least 400 g of pulp in the final preparation.
Blend the potato and water mixture until smooth.
Store in the refrigerator until the time of the lab.
Conducting the Test
Weigh and transfer 50 g of potato pulp into the Nalgene bottle.
Add 0.1 M HCl or 0.1 M NaOH, according to the table below, and mix using a stirring rod.
Check and record the pH using a pH meter.
Record the pH in the table.
Student Group No.pH AdjustmentpH1None 2Add 1 ml HCl 3Add 2 ml HCl 4Add 3 ml HCl 5Add 1 ml NaOH 6Add 2 ml NaOH 7Add 3 ml NaOH
Measuring Catalase Activity
Add 50 mL of 3% hydrogen peroxide to the pulp, plug the Nalgene bottle with the O2 sensor, and immediately start recording oxygen levels using the LabQuest Interface.
Collect oxygen concentration data (ppm) at 30-second intervals for 10 minutes.
Record and transfer the data to a class whiteboard for collective analysis.
Time (minutes)No Change1 ml HCl2 ml HCL3 ml HCL1 ml NaOH2 ml NaOH3 ml NaOH0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Download a PDF Copy of This Experiment!
Data Analysis
Using the collected data, create a graph plotting oxygen concentration (ppm) vs. time (minutes) for each pH level.
For easy comparison, ensure all seven pH levels are plotted on the same graph.
Lab Questions
Based on your graph, which pH level exhibited the highest enzyme activity? Is this supported by literature?
Where does hydrogen peroxide originate from in living organisms? Explain the role of catalase in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
How does pH affect enzyme structure and function? Discuss the impact of pH changes on the active site and overall enzyme activity.
Why do enzymes function within a narrow pH range? Provide an example of another enzyme and its optimum pH.